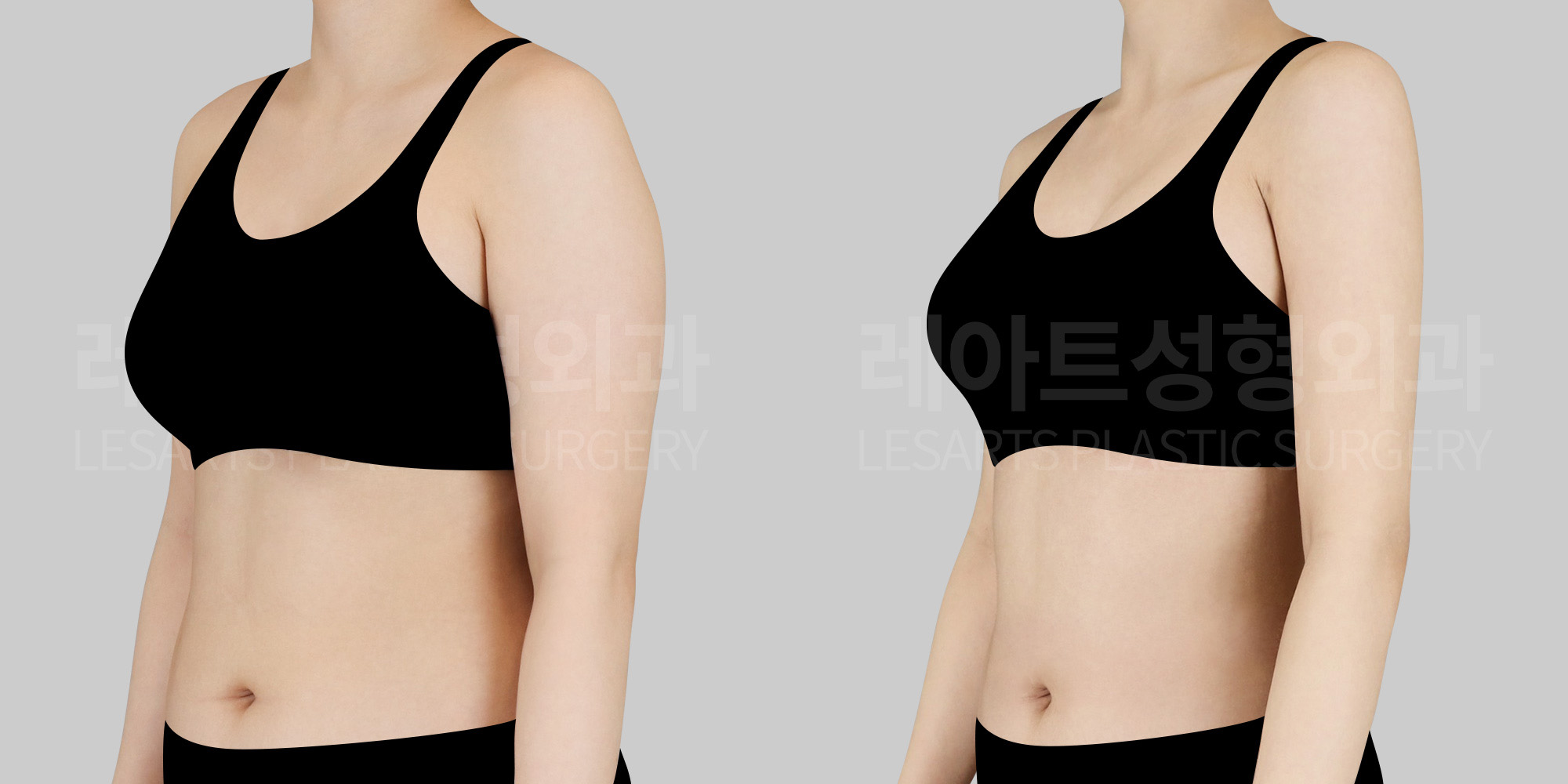
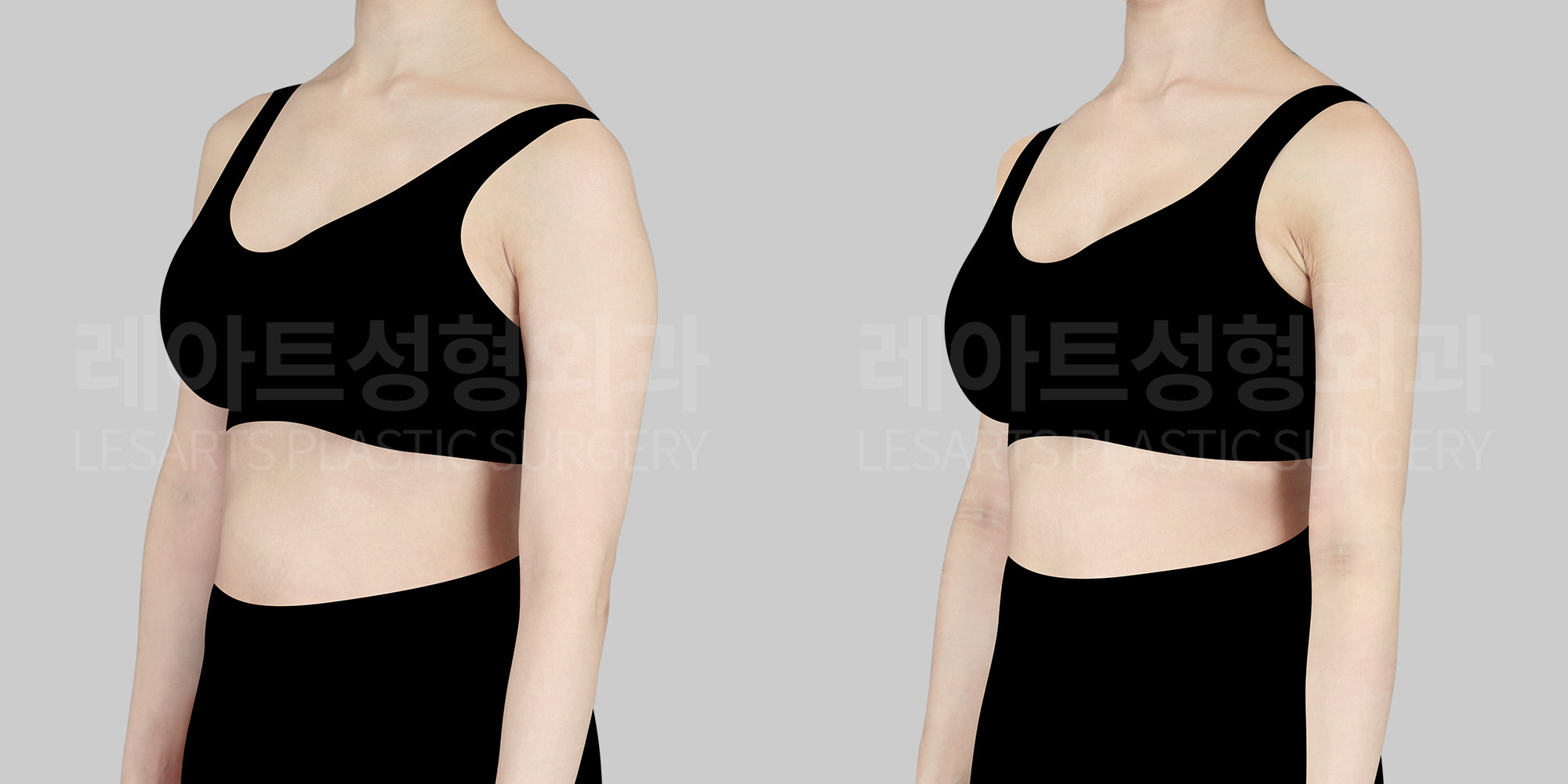
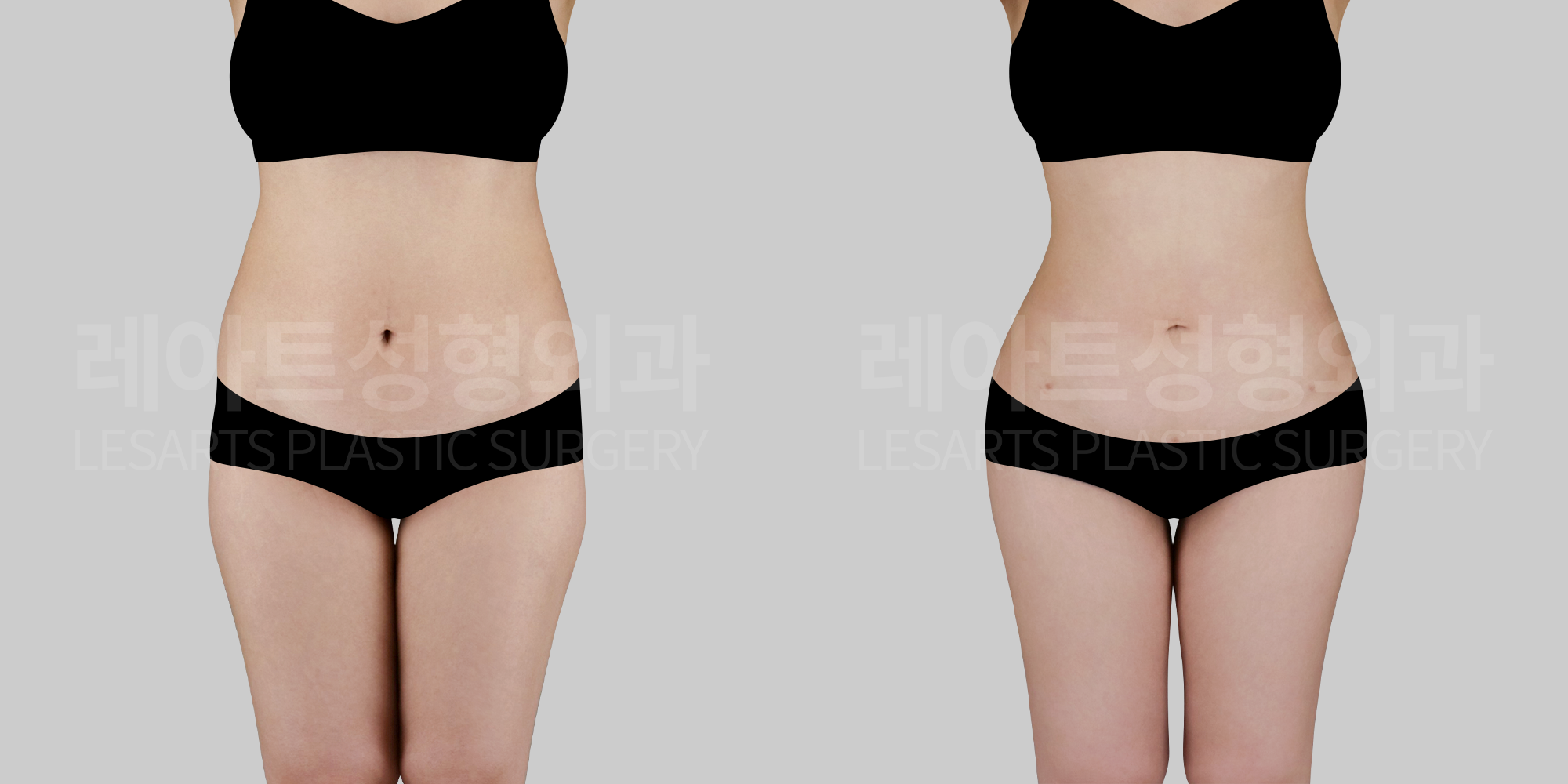
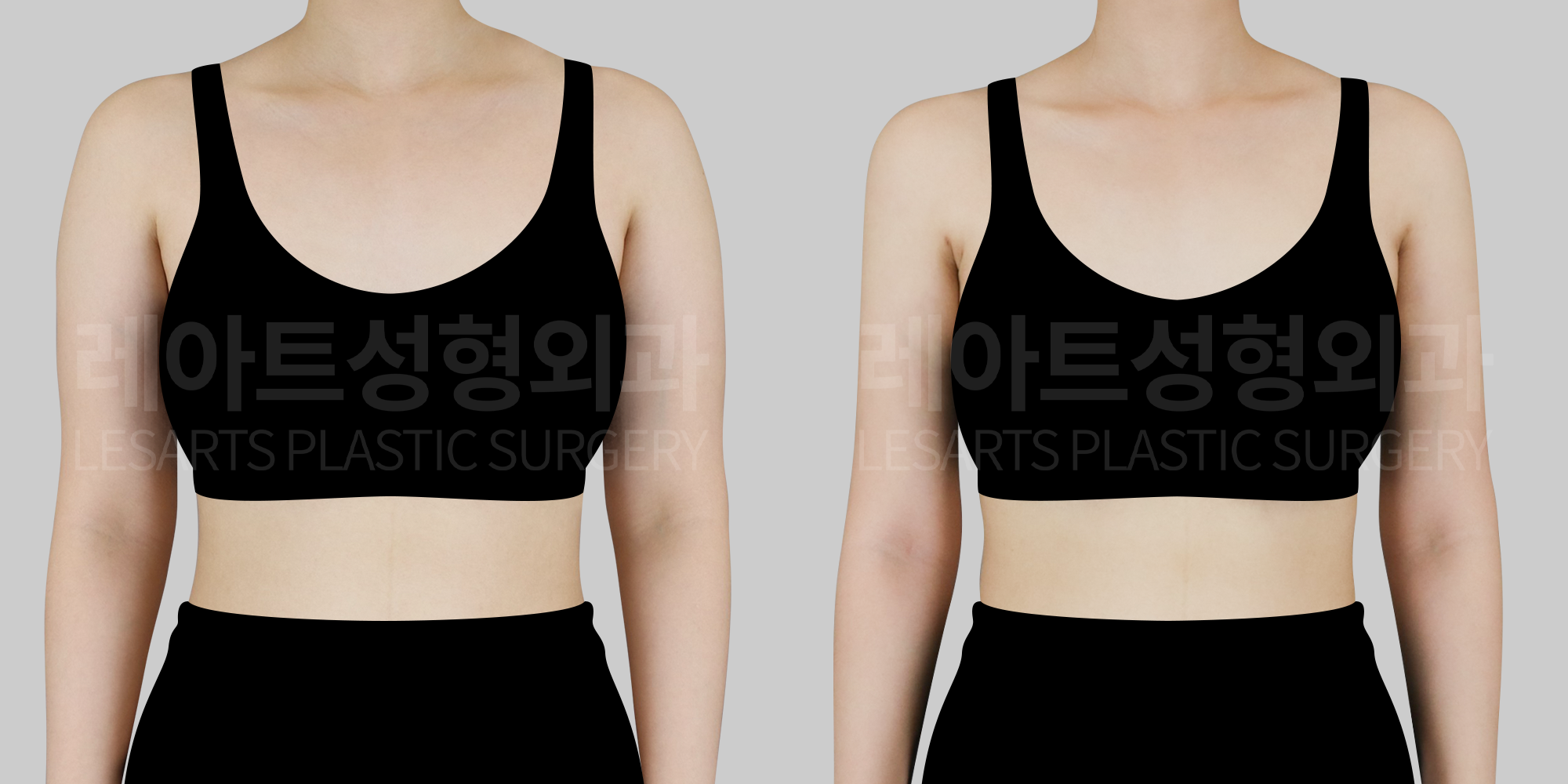
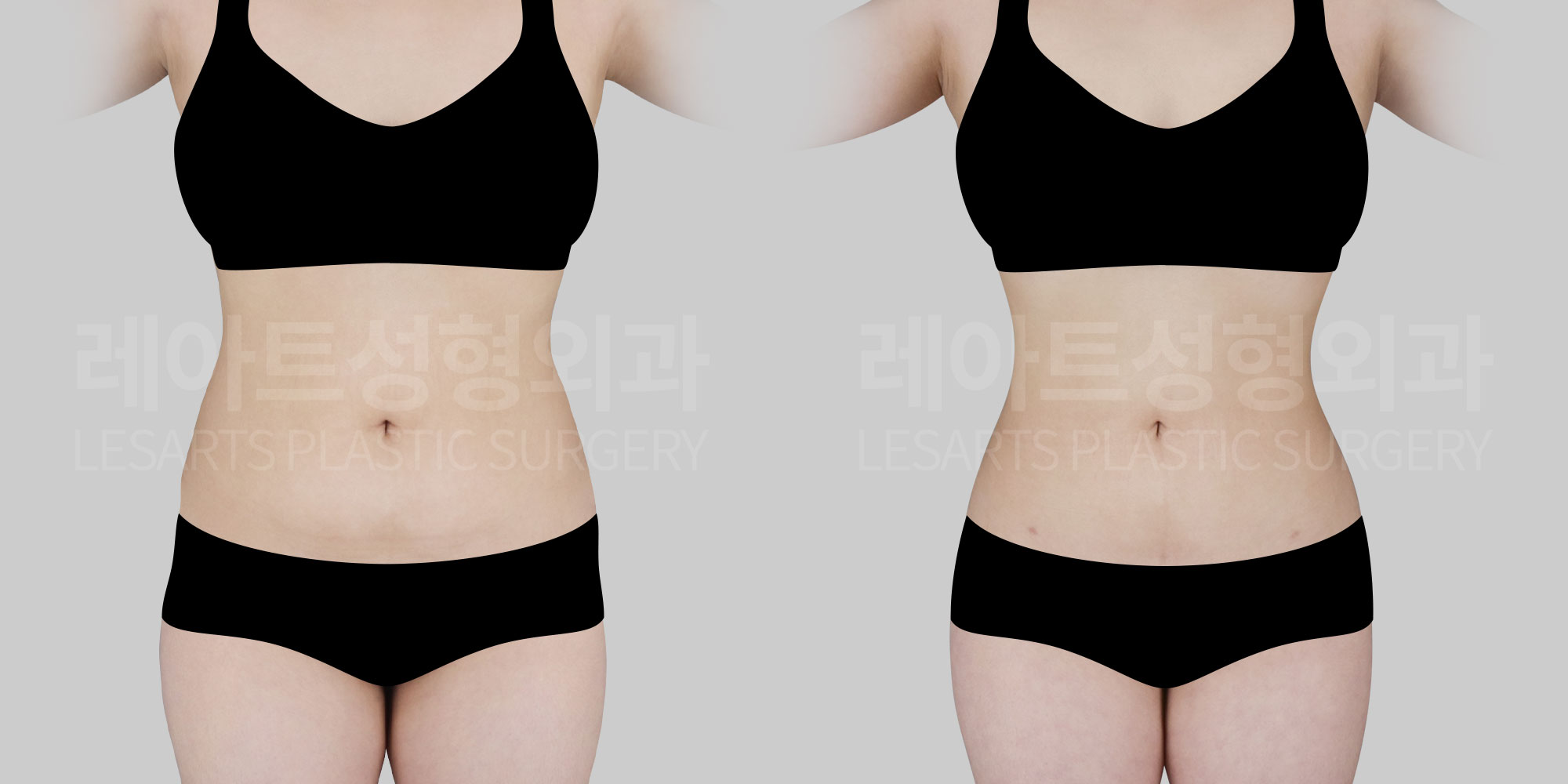
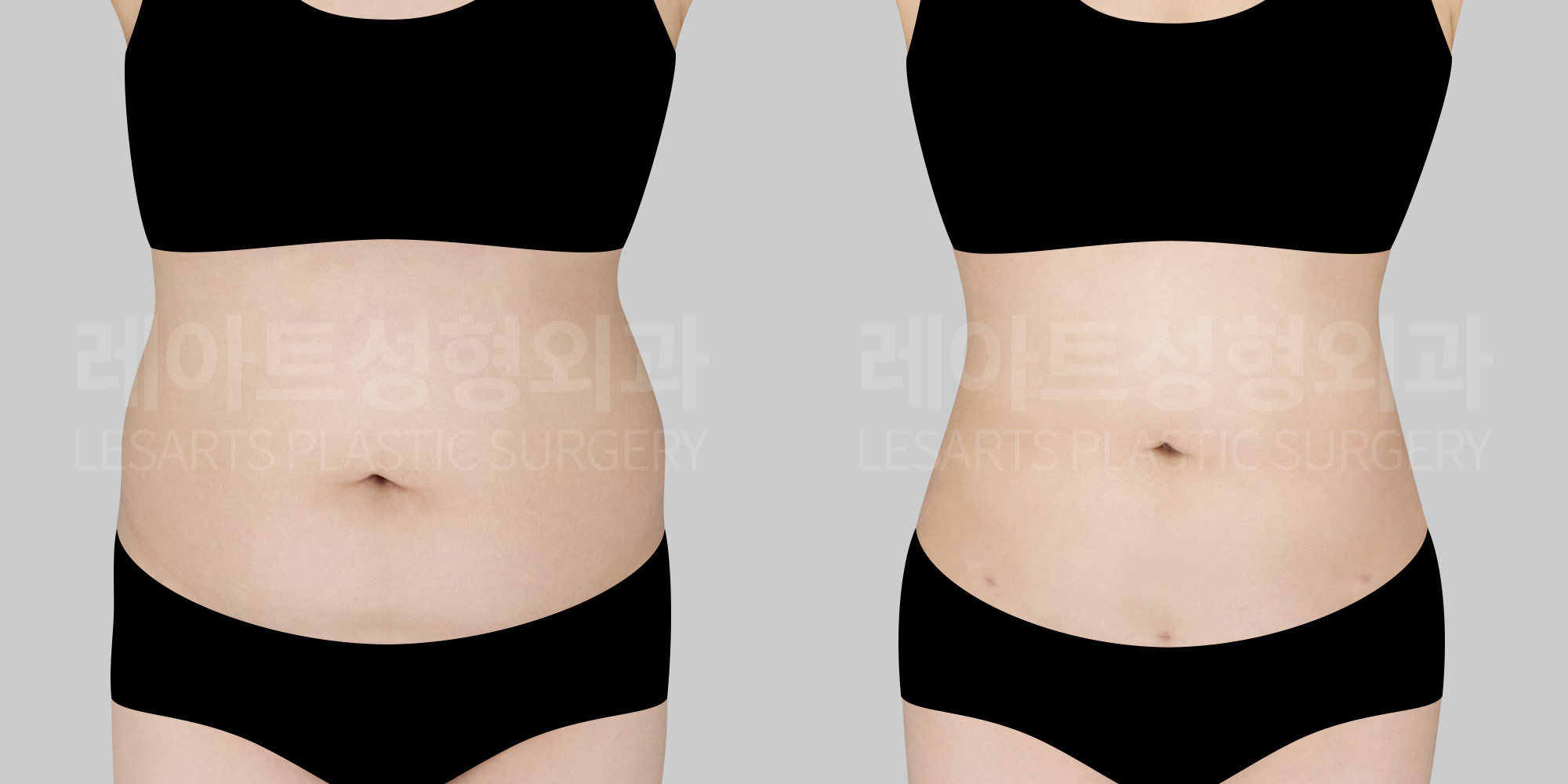
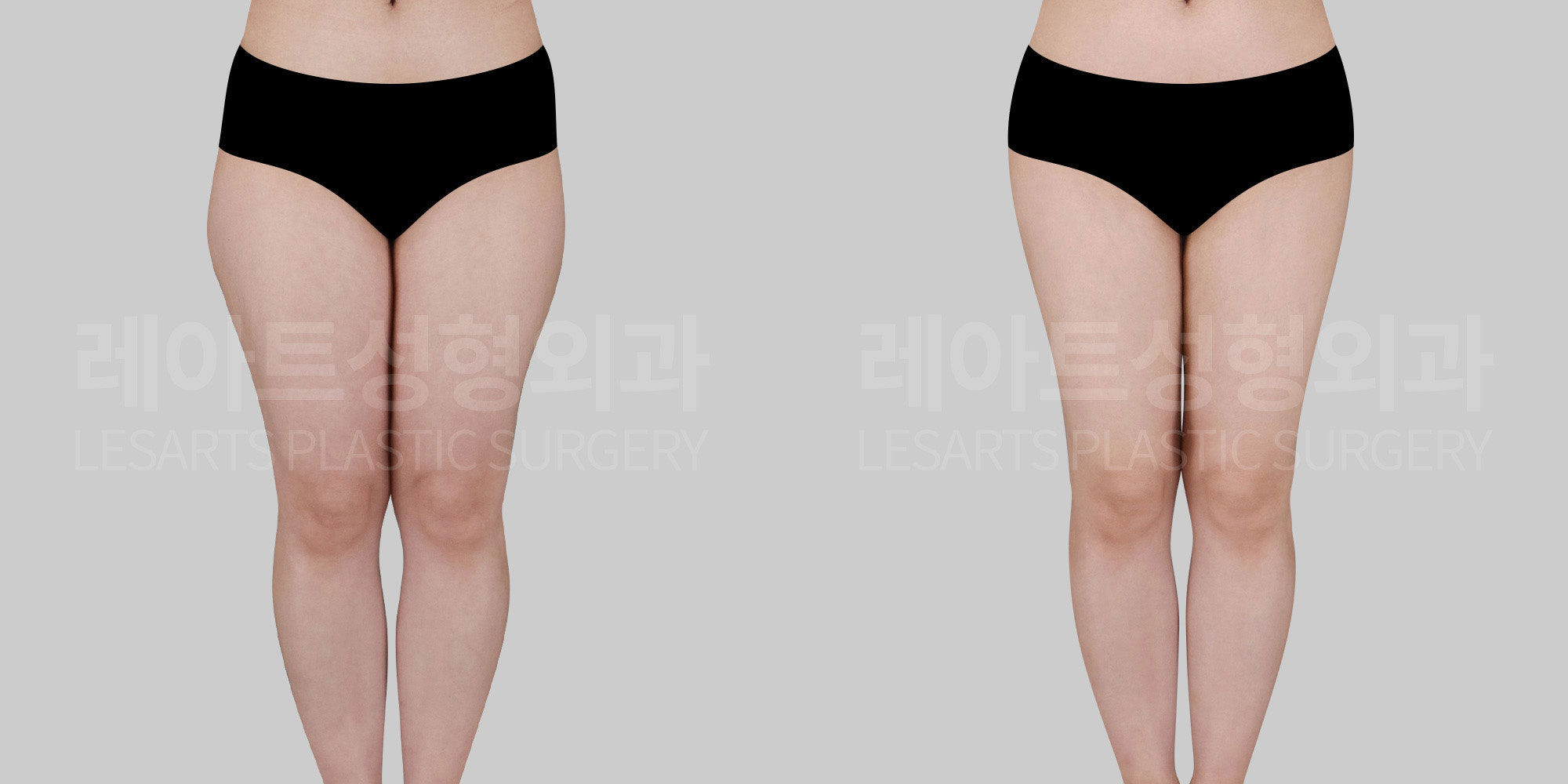
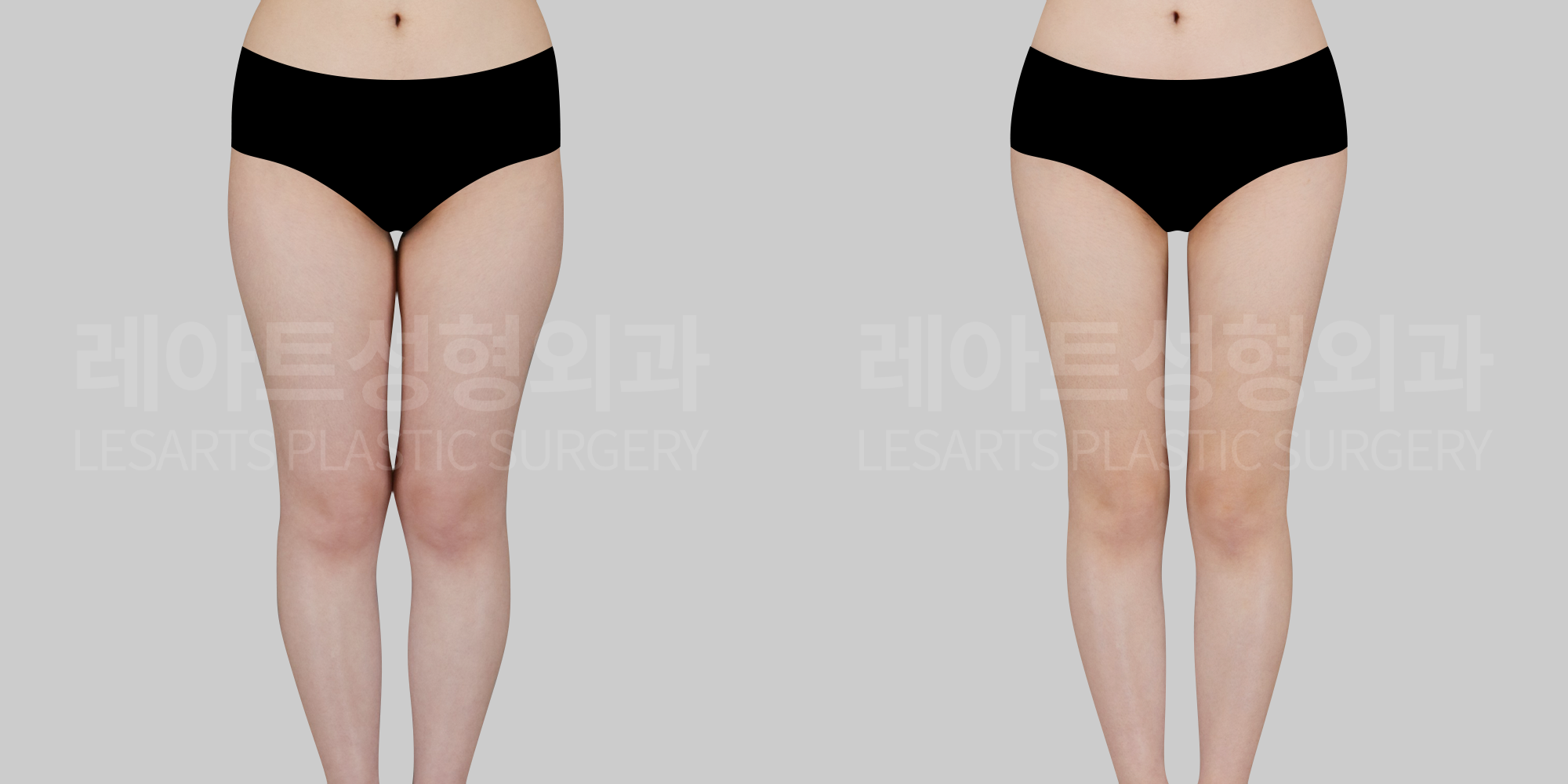
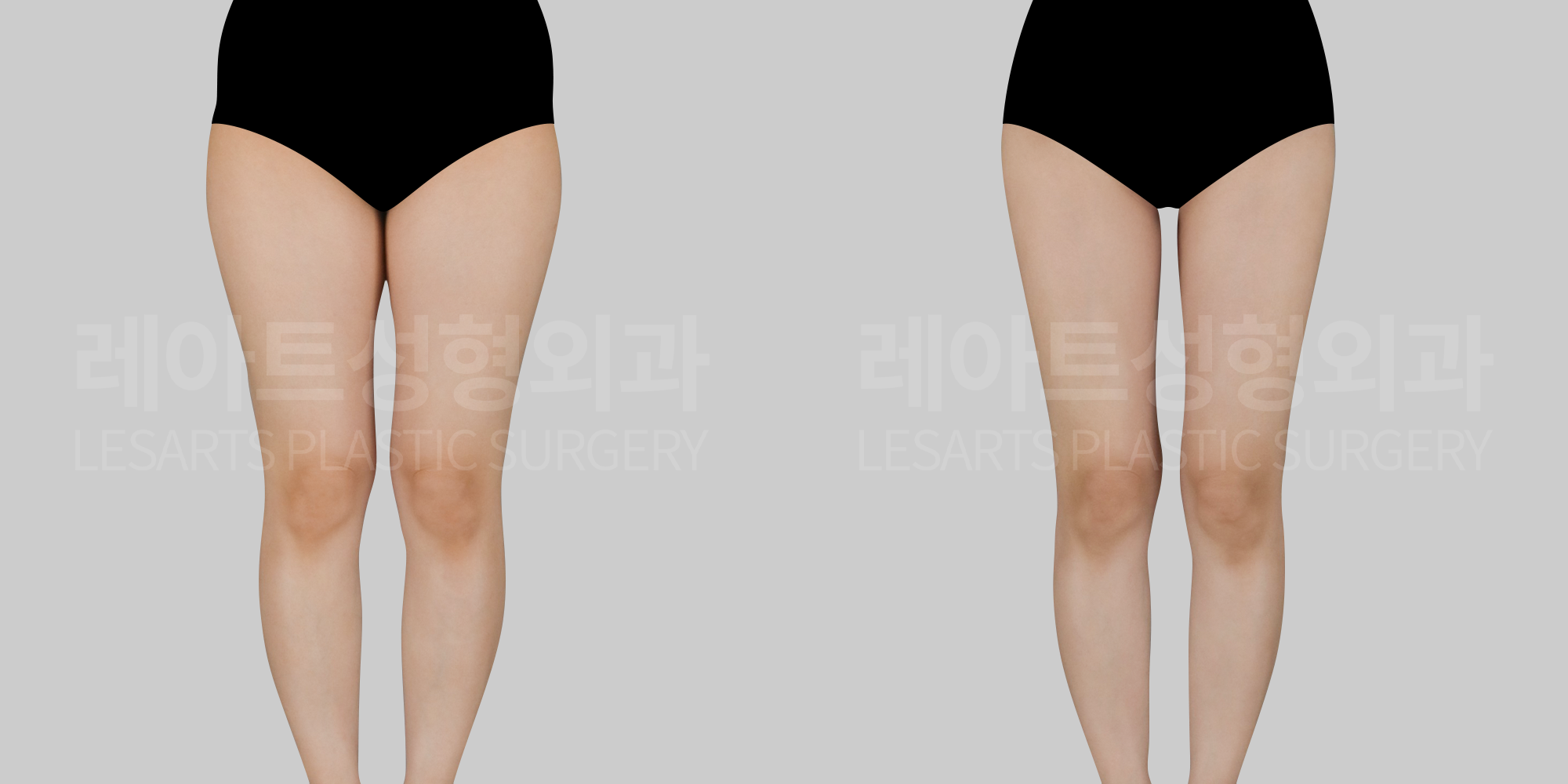
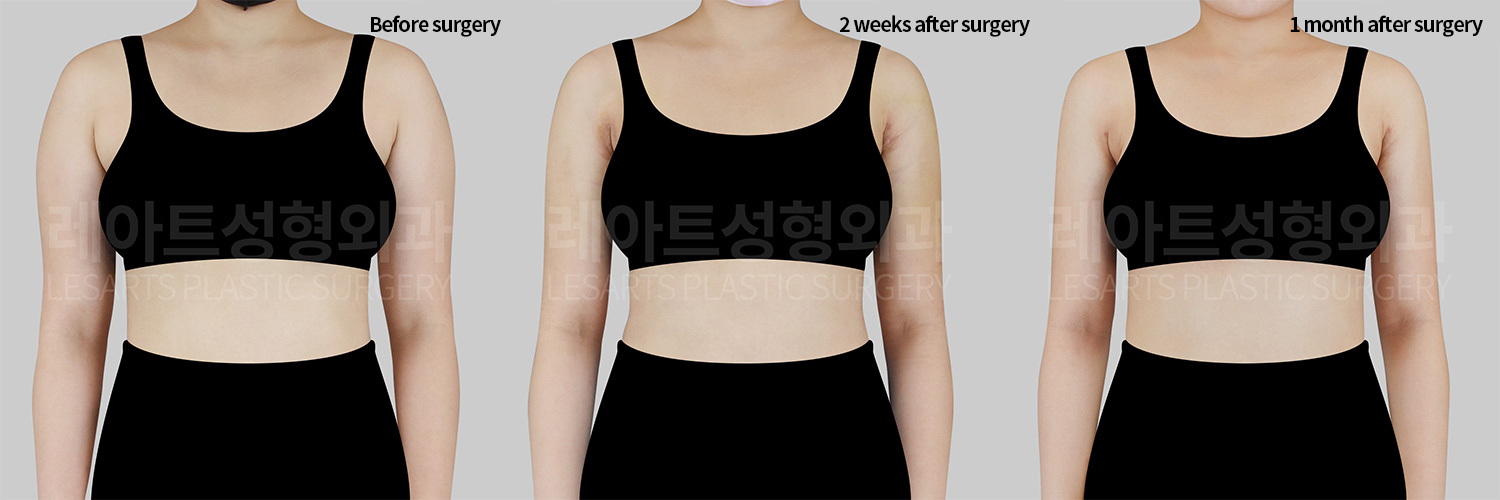
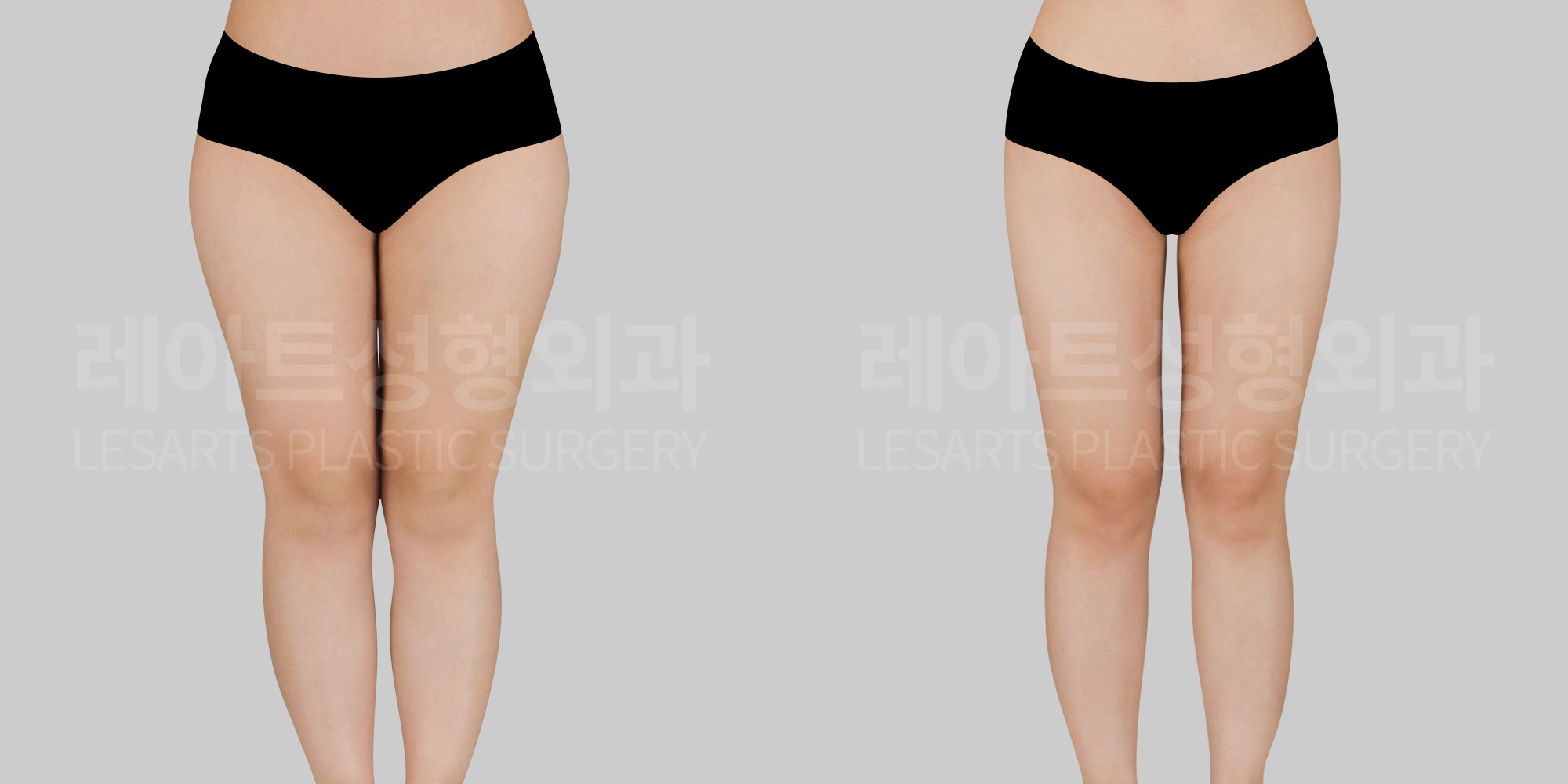
[Body liposuction]Changes in the body after liposuction
Hello, this is Dr. Choi Pyongrim from Lesarts Plastic Surgery.
Liposuction is often thought of
as a procedure that simply removes visible fat.
However, in reality,
it is more accurate to understand it
as a process in which the entire body responds
to the stimulus of surgery
and undergoes a variety of changes.
Beyond changes in body contour where fat is removed,
from immediately after surgery through recovery,
multiple physiological changes occur at the same time,
including alterations in circulation, blood markers,
immune responses, swelling, and inflammatory reactions.
The better these changes are understood,
the faster recovery tends to be,
and the higher patient satisfaction with the results.
In this article,
we will clearly explain the actual changes
that occur in the body after liposuction,
including changes in blood values,
in an easy-to-understand way.

1. Overall physical changes after liposuction
1) Swelling and changes in fluid distribution
Liposuction is a procedure
that removes fat by inserting a fine cannula
into the fat layer.
During this process,
the subcutaneous tissue experiences temporary trauma,
which leads to an increase in interstitial fluid
and results in swelling.
– Immediately after surgery to 1 week:
Localized swelling centered around the surgical area
– 1 to 2 weeks:
Fluid shifts spreading downward due to gravity
– After 3 to 4 weeks:
Gradual reduction as lymphatic circulation recovers
During this period,
changes in body weight are often influenced
more by fluid shifts than by actual fat reduction.

2) Skin and tissue readaptation
The space left after fat removal
does not remain empty.
Over time, surrounding tissues are reorganized,
and the skin adapts to the new volume.
– Early phase:
Induration, where the skin feels firm to the touch
– Recovery phase:
Gradual softening as fibrous tissue is remodeled
– Stabilization phase:
The period when skin elasticity and contours settle
This process varies depending on
the amount and extent of fat removal
and the individual’s skin elasticity.
2. Body changes reflected in blood test results
Although liposuction may appear to be a procedure
that simply removes fat,
the body recognizes it as a form of surgical trauma.
As a result,
meaningful changes can be observed
in blood test values
for a certain period after surgery.
Most of these changes
are normal physiological responses
that occur during the recovery process.
1) Changes in hemoglobin levels
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells
that carries oxygen throughout the body.
When hemoglobin levels decrease,
symptoms such as fatigue and dizziness
may occur.
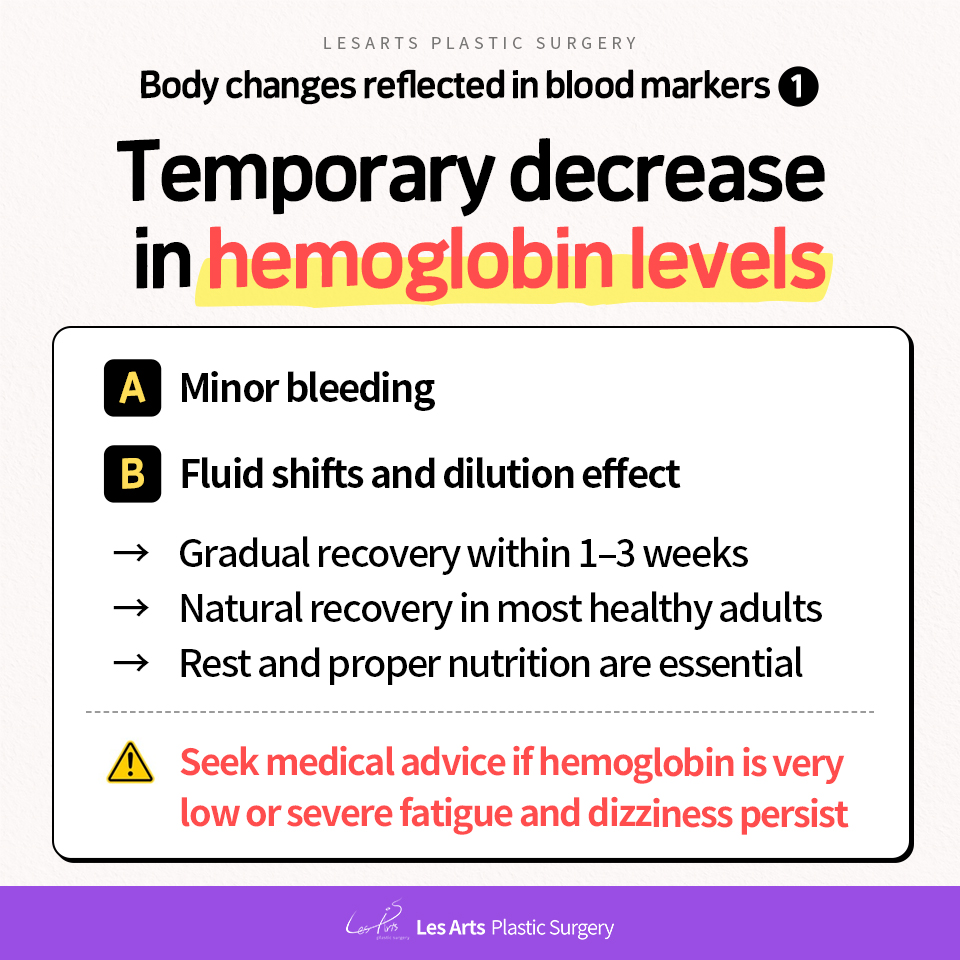
Why do hemoglobin levels decrease after liposuction?
After liposuction,
hemoglobin levels often decrease temporarily.
The reasons are as follows.
A) Microbleeding
During the liposuction process,
small blood vessels are damaged,
causing microscopic bleeding that is not visible to the eye.
This leads to a slight reduction
in red blood cells and hemoglobin.
B) Fluid shifts and dilution effect
Intravenous fluids administered during surgery,
along with postoperative inflammatory responses
that draw fluid into the tissues,
can dilute the blood.
As a result, hemoglobin levels
may appear lower than normal.
When does recovery occur?
– Gradual recovery usually occurs
within 1 to 3 weeks after surgery
– In healthy adults,
levels typically recover naturally
– Adequate rest and proper nutrition
are essential for recovery
📌 Points to note
If hemoglobin levels drop excessively,
or if dizziness and severe fatigue persist,
a consultation with your medical provider is necessary.
2) Changes in white blood cell (WBC) count
What are white blood cells?
White blood cells are cells responsible
for immune defense and inflammatory responses.
Their levels increase
when the body experiences injury or inflammation.
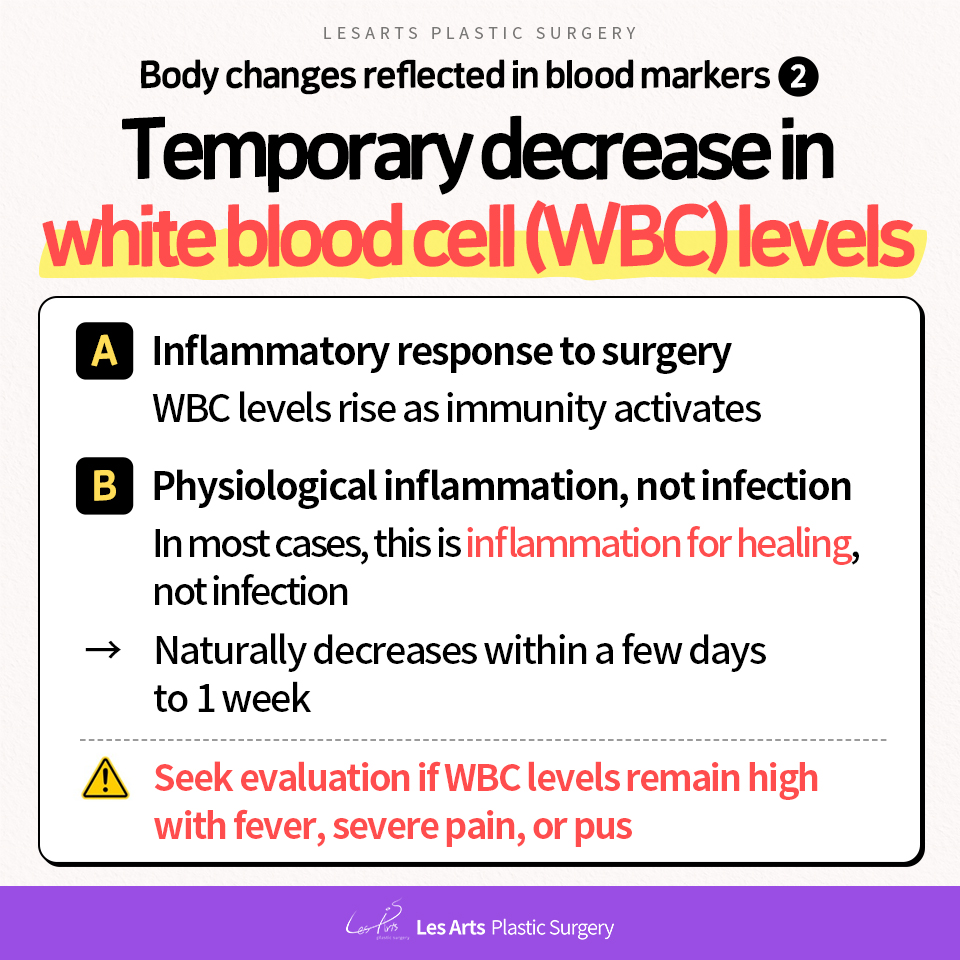
Why does the white blood cell count change after liposuction?
A temporary increase in white blood cell levels
after liposuction is a normal part of recovery.
A) Inflammatory response to surgery
Liposuction involves tissue injury.
The body recognizes this as a wound that needs healing,
which activates immune cells
and leads to an increase in white blood cell count.
B) Physiological inflammation, not infection
In most cases, this is not due to infection,
but a normal inflammatory response for healing.
It may be accompanied by fever, pain, and swelling.
When does it return to normal?
– Usually within a few days to one week after surgery
– As recovery progresses,
white blood cell levels decrease naturally
📌 Points to note
If elevated white blood cell levels persist,
or if they are accompanied by
high fever, severe pain, or pus,
evaluation for possible infection is necessary.
3. Why is blood management before and after surgery
an important factor when choosing a clinic?
The recovery process after liposuction
is not limited to visible swelling and bruising.
It also requires careful management
of invisible changes in blood values
that occur within the body.

– Regular monitoring with blood tests
– Customized recovery care based on swelling and bruising progress
– Medication and IV fluid adjustments when necessary
– Early detection of infection and abnormal reactions
All of these steps require
the careful judgment of experienced medical professionals.
Swelling and bruising after liposuction
are a natural part of the recovery process,
but beneath them lie important signals
in the form of changes in blood values.
At our clinic,
we take responsibility not only for surgical results
but also for the entire recovery process,
using a systematic postoperative care system
to closely monitor each patient’s condition.
If you are looking for liposuction
that prioritizes safety and recovery
rather than just the procedure itself,
we recommend choosing a clinic
with experienced, data-driven medical staff
and thorough postoperative care.